The addition and subtraction of vectors using the graphical method is an intuitive and geometric approach that visually represents the combination or difference of vectors. This method involves drawing vectors as arrows in a coordinate system, allowing for a clear visualisation of the operations. Let's explore the concepts of vector addition and subtraction using the graphical method:
Vector Addition – Graphical Method:
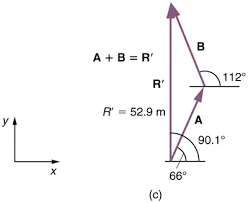
1. Tail-to-Head Method:
-
Step 1: Start by drawing the first vector (A) with its tail at the origin. The arrowhead points in the direction of the vector.
-
Step 2: Draw the second vector (B) with its tail at the head of the first vector. The resulting configuration looks like placing the tail of B at the head of A.
-
Step 3: The sum vector (A + B) is represented by an arrow drawn from the tail of A to the head of B. This new arrow represents the combined effect of both vectors.
2. Graphical Example:
Consider two vectors:
A=[3/2]
B=[−1/4]
Draw A with its tail at the origin and B with its tail at the head of A.
The resultant vector A + B is represented by an arrow from the tail of A to the head of B.
Vector Subtraction – Graphical Method:
1. Tail-to-Tail Method:
Step 1: Draw the first vector (A) with its tail at the origin.
Step 2: Instead of drawing the second vector (B), draw the negative of B (opposite direction) starting from the head of A. This vector is denoted as -B.
Step 3: The resultant vector (A – B) is represented by an arrow drawn from the tail of A to the head of -B.
2. Graphical Example:
Using the same vectors A and B:
A−B=[4 /−2]
Draw A with its tail at the origin.
Draw -B starting from the head of A.
The resultant vector A – B is represented by an arrow from the tail of A to the head of -B.
Key Properties and Takeaways:
1. Commutative Property:
Vector addition is commutative: A + B = B + A.
2. Negative Vectors in Subtraction:
Vector subtraction is related to addition through the use of negative vectors: A – B = A + (-B).
3. Triangle Rule:
The sum of two vectors can be found by forming a triangle with those vectors.
4. Parallelogram Rule:
The sum of two vectors can also be found by forming a parallelogram with those vectors.
Real-world Applications:
1. Navigation:
Vectors can represent displacement, and vector addition is used to calculate the resultant displacement when moving along multiple paths.
2. Forces in Physics:
-
Vectors are extensively used in physics to represent forces. The graphical method aids in determining the net force acting on an object.
3. Velocity in Sports:
-
In sports, the velocity of an object can be represented as a vector. Vector addition helps analyse the combined effect of different velocities.
The graphical method provides a powerful visual tool for understanding vector addition and subtraction. Whether you're navigating a complex path, analysing forces in physics, or calculating velocities in sports, the graphical approach to vector operations remains a valuable and intuitive technique.
CBSE Class 11th Downloadable Resources:
| 1. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Summary | View Page / Download |
| 2. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Books | View Page / Download |
| 3. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Solutions | View Page / Download |
| 4. CBSE Class 11th Exemplar | View Page / Download |
| 5. CBSE Class 11th Previous Year Papers | View Page / Download |
| 6. CBSE Class 11th Sample Papers | View Page / Download |
| 7. CBSE Class 11th Question Bank | View Page / Download |
| 8. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Revision Notes | View Page / Download |
| 9. CBSE Class 11th Last Minutes Preparation Resources | View Page / Download |
| 10. CBSE Class 11th Best Reference Books | View Page / Download |
| 11. CBSE Class 11th Formula Booklet | View Page / Download |
Being in CBSE class 11th and considering the board examinations you must be needing resources to excel in your examinations. At TestprepKart we take great pride in providing CBSE class 11th all study resources in downloadable form for you to keep you going.
Below is the list of all CBSE class 11th Downloads available on TestprepKart for both Indian and NRI students preparing for CBSE class 11th in UAE, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait & Bahrain.
SAMPLE PRACTICE QUESTIONS OF SIGNIFICANT FIGURES :
Q1. What is the Graphical Method for Adding Vectors?
Answer: The graphical method involves representing vectors as arrows in a coordinate system. To add vectors, place the tail of the second vector at the head of the first. The resultant vector is drawn from the tail of the first to the head of the second.
Q2. How is Vector Addition Graphically Illustrated?
Answer: Vector addition is illustrated by placing vectors tip-to-tail. The resultant vector represents the sum of the individual vectors. The length and direction of the resultant vector are determined by the magnitudes and directions of the original vectors.
Q3. What is the Parallelogram Law of Vector Addition?
Answer: The parallelogram law states that the vector sum of two vectors is represented by the diagonal of the parallelogram formed by the vectors. This diagonal represents the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector.
Q4. Can Vectors be Added in any Order?
Answer: Yes, vector addition is commutative. The order in which vectors are added does not affect the result. This property holds true for both the graphical and algebraic methods.
Q5. How is Vector Subtraction Represented Graphically?
Answer: To subtract vectors graphically, the process is similar to addition. However, when subtracting vector B from vector A, the direction of the resultant vector points from the head of B to the head of A.

| Class 11th CBSE Physics Chapters |
| Chapter1: UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS |
| Chapter2: MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE |
| Chapter3: MOTION IN A PLANE |
| > Introduction |
| > Scalars and vectors |
| > Multiplication of vectors by real numbers |
| > Resolution of vectors |
| > Vector addition – analytical method |
| > Motion in a plane |
| > Motion in a plane with constant acceleration |
| > Uniform circular motion |
| Chapter4: LAWS OF MOTION |
| Chapter5: WORK, ENERGY AND POWER |
| Chapter6: SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION |
| Chapter7: GRAVITATION |
| Chapter8: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS |
| Chapter9: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS |
| Chapter10: THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER |
| Chapter12: KINETIC THEORY |
| Chapter13: OSCILLATIONS |
| Chapter14: WAVES |
| Class 11th CBSE Chemistry Chapters |
| Chapter1: SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY |
| Chapter2: STRUCTURE OF ATOMS |
| Chapter3: CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES |
| Chapter4: CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE |
| Chapter5: THERMODYNAMICS |
| Chapter6: EQUILIBRIUM |
| Chapter7: REDOX REACTIONS |
| Chapter8: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY – SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES |
| Chapter9: Hydrocarbons HYDROCARBONS |
| Class 11th CBSE Mathematics chapter |
| Chapter1: SETS |
| Chapter2: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter3: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter4: COMPLEX NUMBER AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS |
| Chapter5: LINEAR INEQUALITIES |
| Chapter6: PERMUTATIONS AND COMBINATIONS |
| Chapter7: BINOMIAL THEOREM |
| Chapter8: SEQUENCES AND SERIES |
| Chapter9: STRAIGHT LINES |
| Chapter10: CONIC SECTIONS |
| Chapter11: INTRODUCTION TO THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY |
| Chapter12: LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES |
| Chapter13:STATISTICS |
| Chapter14: PROBABILITY |
| Class 8 Link soon |
| Class 9 Link soon |
| Class 10 Link soon |
| Class 12 Link soon |
Leave a Reply