Motion is a fundamental aspect of the physical world, and when it occurs in two dimensions, it adds an extra layer of complexity and richness to our understanding. In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating realm of "Motion in a Plane," exploring its principles, equations, and real-world applications.
What Is Motion in a Straight Line?
If an object changes its position with respect to its surroundings with time, then it is called in motion. It is a change in the position of an object over time. Motion in a straight line is nothing but linear motion. As the name suggests, it’s in a particular straight line, thus it can be said that it uses only one dimension.
2. Components of Motion:
In two-dimensional motion, an object's motion can be broken down into horizontal (x-axis) and vertical (y-axis) components. The combination of these components determines the object's trajectory.
Equations of Motion in a Plane:
1. Position Vector:
The position of an object in a plane can be described using a position vector. r=xi^+yj^ , where i^ And j^ are unit vectors along the x and y axes, respectively, (x,y) represents the object's coordinates.
2. Displacement Vector:
The displacement vector d between two points A and B is given by D = rB – rA, representing both magnitude and direction.
3. Velocity and Acceleration:
The velocity vector is the rate of change of displacement, and acceleration a is the rate of change of velocity. These vectors have both magnitude and direction.
What is plane motion ?
Motion in a plane refers to the point where we consider motion in two dimensions as only two dimensions makes a plane. Here, considering the above, we take two axes into consideration – generally X-axis or Y – axes. In an attempt to derive the equation of the motion in a plane, we must know about motion in one direction.
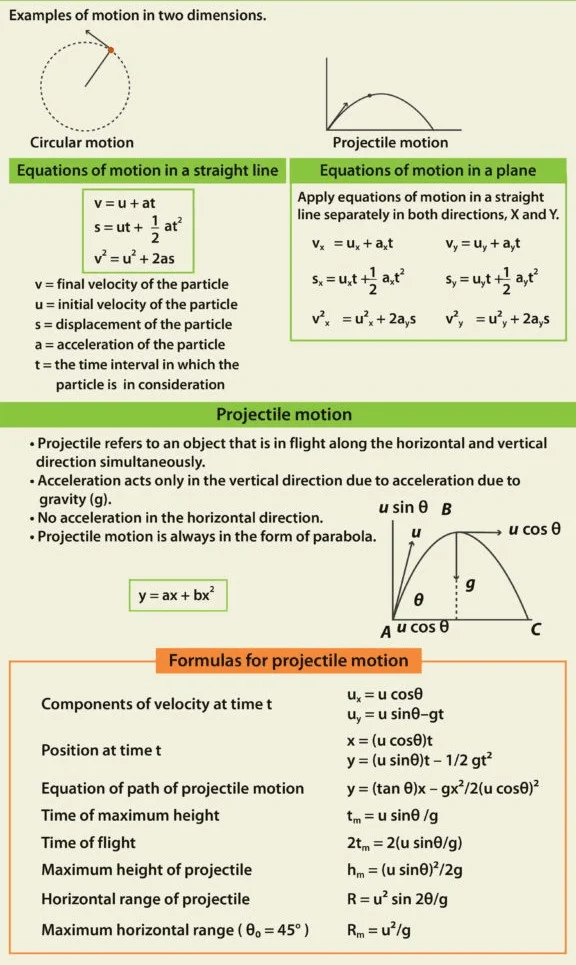
Equations of Plane Motion
The equations of motion in a straight line are:
v = u+at
s = ut+1/2 at²
v2 = u² + 2as
In a plane, we have to apply the same equations separately in both the directions: Y axis and Y-axis. This would give us the equations for motion in a plane.
vy = uy + ayt
sy = uy t +1/2 ay t²
v²y = u²y+2ay s
Where,
-
vy = final velocity of the particle in the y-direction
-
uy = initial velocity of the particle in the y-direction
-
sy = displacement of the particle in the y-direction
-
ay = acceleration of the particle in the y-direction

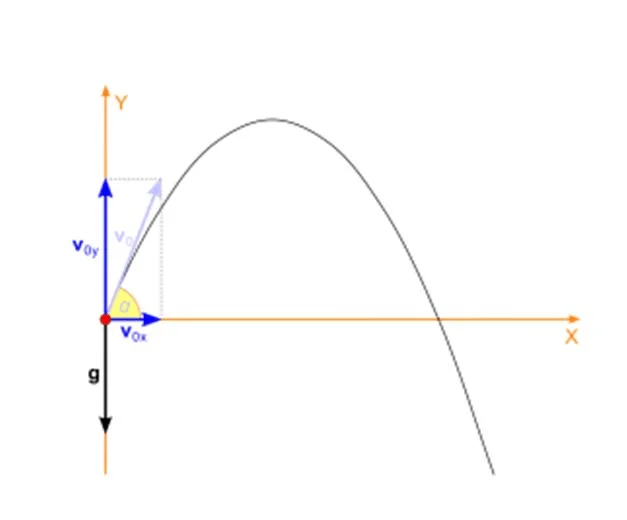
What is projectile motion ?
One of the most common examples of motion in a plane is Projectile motion. In a projectile motion, the only acceleration acting is in the vertical direction which is acceleration due to gravity (g). Therefore, equations of motion can be applied separately in the X-axis and Y-axis to find the unknown parameters.
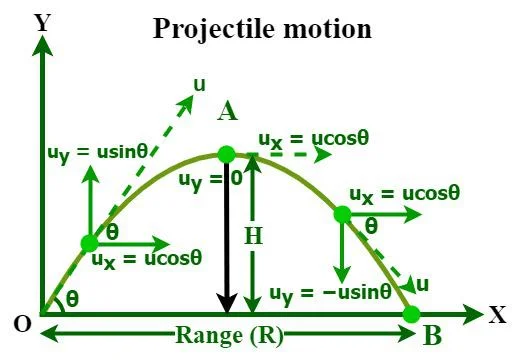
The above diagram represents the motion of an object under the influence of gravity. It is an example of projectile motion (a special case of motion in a plane).
Examples of Two-Dimensional Plane Motion
-
Throwing a ball or a cannonball
-
The motion of a billiard ball on the billiard table.
-
A motion of a shell fired from a gun.
-
A motion of a boat in a river.
-
The motion of the earth around the sun.
CBSE Class 11th Downloadable Resources:
| 1. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Summary | View Page / Download |
| 2. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Books | View Page / Download |
| 3. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Solutions | View Page / Download |
| 4. CBSE Class 11th Exemplar | View Page / Download |
| 5. CBSE Class 11th Previous Year Papers | View Page / Download |
| 6. CBSE Class 11th Sample Papers | View Page / Download |
| 7. CBSE Class 11th Question Bank | View Page / Download |
| 8. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Revision Notes | View Page / Download |
| 9. CBSE Class 11th Last Minutes Preparation Resources | View Page / Download |
| 10. CBSE Class 11th Best Reference Books | View Page / Download |
| 11. CBSE Class 11th Formula Booklet | View Page / Download |
Being in CBSE class 11th and considering the board examinations you must be needing resources to excel in your examinations. At TestprepKart we take great pride in providing CBSE class 11th all study resources in downloadable form for you to keep you going.
Below is the list of all CBSE class 11th Downloads available on TestprepKart for both Indian and NRI students preparing for CBSE class 11th in UAE, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait & Bahrain.
SAMPLE PRACTICE QUESTIONS OF SIGNIFICANT FIGURES :
Q1. What is Motion in a Plane?
Answer: Motion in a plane refers to the movement of an object where its position is described by two coordinates (usually x and y) in a two-dimensional space.
Q2. How is Motion in a Plane Different from Motion in a Straight Line?
Answer: Motion in a straight line occurs along a single dimension (usually the x-axis), while motion in a plane involves movement in two dimensions (both x and y axes).
Q3. What are the Two Components of Motion in a Plane?
Answer: Motion in a plane has two components: horizontal motion (along the x-axis) and vertical motion (along the y-axis).
Q4. How is Displacement Defined in Motion in a Plane?
Answer: Displacement in motion in a plane is a vector quantity defined by both magnitude and direction. It is the change in position from the initial to the final point.
Q5. What is Projectile Motion?
Answer: Projectile motion is a specific type of motion in a plane where an object is launched into the air and follows a curved path under the influence of gravity.

| Class 11th CBSE Physics Chapters |
| Chapter1: UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS |
| Chapter2: MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE |
| Chapter3: MOTION IN A PLANE |
| > Introduction |
| > Scalars and vectors |
| > Multiplication of vectors by real numbers |
| > Addition and subtraction of vectors – graphical method |
| > Resolution of vectors |
| > Vector addition – analytical method |
| > Motion in a plane with constant acceleration |
| > Uniform circular motion |
| Chapter4: LAWS OF MOTION |
| Chapter5: WORK, ENERGY AND POWER |
| Chapter6: SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION |
| Chapter7: GRAVITATION |
| Chapter8: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS |
| Chapter9: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS |
| Chapter10: THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER |
| Chapter12: KINETIC THEORY |
| Chapter13: OSCILLATIONS |
| Chapter14: WAVES |
| Class 11th CBSE Chemistry Chapters |
| Chapter1: SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY |
| Chapter2: STRUCTURE OF ATOMS |
| Chapter3: CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES |
| Chapter4: CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE |
| Chapter5: THERMODYNAMICS |
| Chapter6: EQUILIBRIUM |
| Chapter7: REDOX REACTIONS |
| Chapter8: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY – SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES |
| Chapter9: Hydrocarbons HYDROCARBONS |
| Class 11th CBSE Mathematics chapter |
| Chapter1: SETS |
| Chapter2: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter3: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter4: COMPLEX NUMBER AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS |
| Chapter5: LINEAR INEQUALITIES |
| Chapter6: PERMUTATIONS AND COMBINATIONS |
| Chapter7: BINOMIAL THEOREM |
| Chapter8: SEQUENCES AND SERIES |
| Chapter9: STRAIGHT LINES |
| Chapter10: CONIC SECTIONS |
| Chapter11: INTRODUCTION TO THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY |
| Chapter12: LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES |
| Chapter13: STATISTICS |
| Chapter14: PROBABILITY |
| Class 8 Link soon |
| Class 9 Link soon |
| Class 10 Link soon |
| Class 12 Link soon |
Leave a Reply