What Is Uniform Circular Motion?
Uniform Circular Motion is a specific type of motion in which an object travels along a circular path at a constant speed.This concept is fundamental in physics and is applicable to various scenarios, from celestial bodies orbiting in space to objects moving in circular paths on Earth.
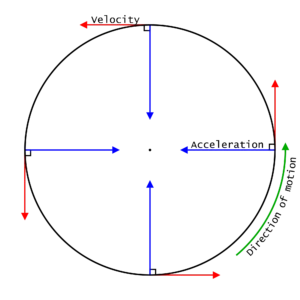
Key Components of Uniform Circular Motion:
Constant Speed: The object in uniform circular motion maintains a consistent speed throughout its journey. This means that the magnitude of its velocity (a vector quantity representing both speed and direction) remains unchanged. The direction of the velocity, however, is continually changing as it is always tangent to the circle at any given point.
Centripetal Acceleration: Despite the constant speed, there is an acceleration involved in uniform circular motion. This acceleration is called centripetal acceleration and is directed toward the centre of the circle. It is responsible for keeping the object in its circular path. The formula for centripetal acceleration (ae) is given by ac=v2 , where v is the speed of the object, and r is the radius of the circular path.
Centripetal Force: The force responsible for providing the centripetal acceleration is called centripetal force (Fc). In many cases, gravity acts as the centripetal force, especially in the context of celestial bodies in orbit. The formula for centripetal force is Fc=m⋅ac, where m is the mass of the object.
Examples of Uniform Circular Motion:
Planetary Orbits:
-
Example: The Earth revolving around the Sun.
-
Explanation: Planets in our solar system, including Earth, exhibit uniform circular motion as they orbit the Sun. The gravitational force between the Sun and the planet acts as the centripetal force, keeping the planet in its nearly circular orbit.


Satellite Orbits:
-
Example: Communication satellites in geostationary orbit.
-
Explanation: Satellites in geostationary orbit circle the Earth at a constant speed and altitude, ensuring that they remain positioned above a fixed point on the Earth's surface. This is a form of uniform circular motion.
Whirling a Ball on a String:
-
Example: Swinging a ball around in a horizontal circle.
-
Explanation: When you swing a ball attached to a string in a horizontal circle, the ball undergoes uniform circular motion. The tension in the string provides the centripetal force necessary to keep the ball in its circular path.
Carousels:
-
Example: Amusement park carousels.
-
Explanation: The rotating platform of a carousel spins at a constant speed, providing riders with a classic example of uniform circular motion. The centripetal force is generated by the mechanical structure of the ride.
Ferris Wheels:
-
Example: Giant Ferris wheels.
-
Explanation: The cabins on a Ferris wheel move in a circular path at a constant speed, creating a sense of uniform circular motion for the riders. The wheel's structure ensures a consistent rotational speed.
CBSE Class 11th Downloadable Resources:
| 1. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Summary | View Page / Download |
| 2. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Books | View Page / Download |
| 3. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Solutions | View Page / Download |
| 4. CBSE Class 11th Exemplar | View Page / Download |
| 5. CBSE Class 11th Previous Year Papers | View Page / Download |
| 6. CBSE Class 11th Sample Papers | View Page / Download |
| 7. CBSE Class 11th Question Bank | View Page / Download |
| 8. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Revision Notes | View Page / Download |
| 9. CBSE Class 11th Last Minutes Preparation Resources | View Page / Download |
| 10. CBSE Class 11th Best Reference Books | View Page / Download |
| 11. CBSE Class 11th Formula Booklet | View Page / Download |
Being in CBSE class 11th and considering the board examinations you must be needing resources to excel in your examinations. At TestprepKart we take great pride in providing CBSE class 11th all study resources in downloadable form for you to keep you going.
Below is the list of all CBSE class 11th Downloads available on TestprepKart for both Indian and NRI students preparing for CBSE class 11th in UAE, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait & Bahrain.
SAMPLE PRACTICE QUESTIONS OF SIGNIFICANT FIGURES :
Q1. What is Uniform Circular Motion?
Answer: Uniform Circular Motion is the motion of an object in a circular path at a constant speed. The object's speed remains the same, but its direction continuously changes, creating circular motion.
Q2. How is Uniform Circular Motion Different from Linear Motion?
Answer: In linear motion, an object moves in a straight line, while in uniform circular motion, it follows a circular path. The key difference lies in the constant change of direction in circular motion.
Q3. What Keeps an Object in Uniform Circular Motion?
Answer: An object in uniform circular motion is kept in its path by a centripetal force. This force acts toward the center of the circle and is responsible for changing the object's direction.
Q4. Is the Speed Constant in Uniform Circular Motion?
Answer: Yes, the speed of an object in uniform circular motion is constant. However, since the direction changes continuously, it experiences acceleration known as centripetal acceleration.
Q5. What is Centripetal Acceleration?
Answer: Centripetal acceleration is the acceleration directed toward the center of the circular path. It is always perpendicular to the object's velocity and is responsible for keeping the object in its circular motion.

| Class 11th CBSE Physics Chapters |
| Chapter1: UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS |
| Chapter2: MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE |
| Chapter3: MOTION IN A PLANE |
| > Introduction |
| > Scalars and vectors |
| > Multiplication of vectors by real numbers |
| > Addition and subtraction of vectors – graphical method |
| > Resolution of vectors |
| > Vector addition – analytical method |
| > Motion in a plane |
| > Motion in a plane with constant acceleration |
| > Projectile motion |
| Chapter4: LAWS OF MOTION |
| Chapter5: WORK, ENERGY AND POWER |
| Chapter6: SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION |
| Chapter7: GRAVITATION |
| Chapter8: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS |
| Chapter9: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS |
| Chapter10: THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER |
| Chapter12: KINETIC THEORY |
| Chapter13: OSCILLATIONS |
| Chapter14: WAVES |
| Class 11th CBSE Chemistry Chapters |
| Chapter1: SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY |
| Chapter2: STRUCTURE OF ATOMS |
| Chapter3: CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES |
| Chapter4: CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE |
| Chapter5: THERMODYNAMICS |
| Chapter6: EQUILIBRIUM |
| Chapter7: REDOX REACTIONS |
| Chapter8: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY – SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES |
| Chapter9: Hydrocarbons HYDROCARBONS |
| Class 11th CBSE Mathematics chapter |
| Chapter1: SETS |
| Chapter2: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter3: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter4: COMPLEX NUMBER AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS |
| Chapter5: LINEAR INEQUALITIES |
| Chapter6: PERMUTATIONS AND COMBINATIONS |
| Chapter7: BINOMIAL THEOREM |
| Chapter8: SEQUENCES AND SERIES |
| Chapter9: STRAIGHT LINES |
| Chapter10: CONIC SECTIONS |
| Chapter11: INTRODUCTION TO THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY |
| Chapter12: LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES |
| Chapter13: STATISTICS |
| Chapter14: PROBABILITY |
| Class 8 Link soon |
| Class 9 Link soon |
| Class 10 Link soon |
| Class 12 Link soon |
Leave a Reply