Springs are remarkable devices that play a fundamental role in our daily lives, from the suspension systems of vehicles to the functioning of everyday items like pens and mattresses. Behind the fascinating characteristics of springs lies a concept central to their behaviour—the potential energy stored within them. In this exploration, we will delve into the intricacies of the potential energy of springs, uncovering the underlying physics and practical applications that make them indispensable.
What is Springs?
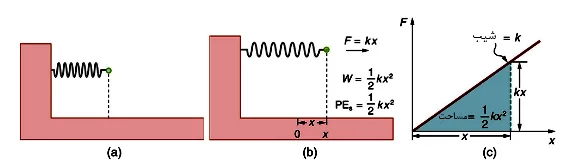
Springs are elastic objects that deform under the influence of an external force and return to their original shape when the force is removed. This ability to store and release energy is attributed to the potential energy inherent in the spring.
Hooke's Law:
The potential energy of a spring is governed by Hooke's Law, named after the 17th-century physicist Robert Hooke. This law states that the force required to compress or extend a spring by a distance x is directly proportional to x. Mathematically, it is expressed as F=−kx, where F is the force applied, k is the spring constant, and x is the displacement from the equilibrium position.

Potential Energy Equation:
The potential energy (PE) stored in a spring can be derived from Hooke's Law. For a compressed or stretched spring, the potential energy is given by PE=1/2kx2 , where k is the spring constant and x is the displacement from the equilibrium position.
Deriving the Equation:
To understand the potential energy equation, let's consider a spring at its equilibrium position. When a force is applied, causing the spring to compress or stretch by a displacement
x, work is done against the spring force.
Work Done:
The work done (W) in compressing or extending the spring is the integral of force with respect to displacement:
w=∫0xFdx
Substituting Hooke's Law (F=−kx), we get:
W=∫0x(−kx) dx
Evaluating the integral, we find w=1/2kx2 , which is the potential energy stored in the spring.
Mechanical Springs:
Springs are extensively used in mechanical systems, providing shock absorption, storing and releasing energy, and maintaining equilibrium.

Automotive Suspension Systems:
Coil springs in vehicle suspensions store potential energy to absorb shocks from uneven road surfaces, ensuring a smoother ride.
Elastic Potential Energy in Toys:
Springs are commonly found in toys like pogo sticks and wind-up toys, utilising elastic potential energy for dynamic movements.
Mechanical Watches:
Springs power the mechanisms in mechanical watches, storing energy when wound and releasing it slowly to drive the watch's components.
Biomechanics:
Understanding the potential energy of springs is crucial in biomechanics, especially in analysing the mechanics of human joints and muscles.
CBSE Class 11th Downloadable Resources:
| 1. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Summary | View Page / Download |
| 2. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Books | View Page / Download |
| 3. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Solutions | View Page / Download |
| 4. CBSE Class 11th Exemplar | View Page / Download |
| 5. CBSE Class 11th Previous Year Papers | View Page / Download |
| 6. CBSE Class 11th Sample Papers | View Page / Download |
| 7. CBSE Class 11th Question Bank | View Page / Download |
| 8. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Revision Notes | View Page / Download |
| 9. CBSE Class 11th Last Minutes Preparation Resources | View Page / Download |
| 10. CBSE Class 11th Best Reference Books | View Page / Download |
| 11. CBSE Class 11th Formula Booklet | View Page / Download |
Being in CBSE class 11th and considering the board examinations you must be needing resources to excel in your examinations. At TestprepKart we take great pride in providing CBSE class 11th all study resources in downloadable form for you to keep you going.
Below is the list of all CBSE class 11th Downloads available on TestprepKart for both Indian and NRI students preparing for CBSE class 11th in UAE, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait & Bahrain.
SAMPLE PRACTICE QUESTIONS OF SIGNIFICANT FIGURES:
Q1. What is Potential Energy in the Context of a Spring?
Answer: In the context of a spring, potential energy refers to the energy stored in the spring when it is compressed or stretched from its equilibrium position. This stored energy can be released and converted into kinetic energy when the spring is allowed to return to its original position.
Q2. How is Potential Energy Calculated for a Spring?
Answer: The potential energy (PE) stored in a spring is calculated using Hooke's Law: 2PE=21kx2, where k is the spring constant and x is the displacement from the equilibrium position.
Q3. What is Hooke's Law, and How Does it Relate to Potential Energy?
Answer: Hooke's Law states that the force required to compress or stretch a spring is directly proportional to the displacement from its equilibrium position. The potential energy formula is derived from Hooke's Law.
Q4. What Factors Affect the Potential Energy Stored in a Spring?
Answer: The potential energy stored in a spring is affected by two main factors: the spring constant (k) and the displacement (x). A stiffer spring (higher k) or a greater displacement results in more stored potential energy.
Q5. Can a Compressed Spring Have Negative Potential Energy?
Answer: No, potential energy is a scalar quantity, and it is always non-negative. However, the choice of reference point can affect the sign of potential energy changes.
| Class 11th CBSE Physics Chapters |
| Chapter1: UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS |
| Chapter2: MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE |
| Chapter3: MOTION IN A PLANE |
| Chapter4: LAWS OF MOTION |
| Chapter5: WORK, ENERGY AND POWER |
| > Introduction |
| > Notions of work and kinetic energy: The work-energy theorem |
| > Work |
| > Kinetic energy |
| > Work done by a variable force |
| > The concept of potential energy |
| > The conservation of mechanical energy |
| > Power |
| > Collisions |
| Chapter6: SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION |
| Chapter7: GRAVITATION |
| Chapter8: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS |
| Chapter9: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS |
| Chapter10: THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER |
| Chapter12: KINETIC THEORY |
| Chapter13: OSCILLATIONS |
| Chapter14: WAVES |
| Class 11th CBSE Chemistry Chapters |
| Chapter1: SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY |
| Chapter2: STRUCTURE OF ATOMS |
| Chapter3: CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES |
| Chapter4: CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE |
| Chapter5: THERMODYNAMICS |
| Chapter6: EQUILIBRIUM |
| Chapter7: REDOX REACTIONS |
| Chapter8: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY – SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES |
| Chapter9: Hydrocarbons HYDROCARBONS |
| Class 11th CBSE Mathematics chapter |
| Chapter1: SETS |
| Chapter2: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter3: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter4: COMPLEX NUMBER AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS |
| Chapter5: LINEAR INEQUALITIES |
| Chapter6: PERMUTATIONS AND COMBINATIONS |
| Chapter7: BINOMIAL THEOREM |
| Chapter8: SEQUENCES AND SERIES |
| Chapter9: STRAIGHT LINES |
| Chapter10: CONIC SECTIONS |
| Chapter11: INTRODUCTION TO THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY |
| Chapter12: LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES |
| Chapter13: STATISTICS |
| Chapter14: PROBABILITY |
| Class 8 Link soon |
| Class 9 Link soon |
| Class 10 Link soon |
| Class 12 Link soon |
Leave a Reply