Reproduction is a fundamental characteristic of living organisms, ensuring the continuity of life and the preservation of genetic information across generations. The diverse mechanisms through which organisms reproduce reflect the incredible adaptability and variety of life forms on Earth. From simple unicellular organisms to complex multicellular organisms, reproduction plays a central role in the perpetuation and evolution of species.
Unveiling the Wonders of Life: Exploring the Intricate Ways in Which Organisms Reproduce
Reproduction is essential for the survival and persistence of species. It allows organisms to produce offspring, passing on their genetic material to ensure the continuity of their lineage. The ability to reproduce also contributes to the adaptability and resilience of populations in response to changing environmental conditions.
How do Organisms Reproduce?
The organisms reproduce in two ways:
-
Asexual Reproduction– In this process, only a single parent is involved and no gamete formation takes place.
-
Sexual Reproduction– In this process, two parents are involved and gamete formation takes place. Meiosis is an important step in sexual reproduction.
Explore more about Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction is further divided into:
-
Fission
-
Budding
-
Vegetative propagation
-
Regeneration
-
Spore formation
Fission :
This process takes place in unicellular organisms. It is of two types:
-
Binary Fission– The organisms reproduce by binary fission only when adequate amounts of food and moisture is available. In this, the mother cell divides into two daughter cells, each containing a nucleus. Amoeba divides by binary fission.
-
Multiple Fission– The unicellular organisms reproduce by multiple fission when the conditions are unfavourable with no proper amounts of food, moisture, and temperature. In this, the organism forms a cyst around itself. The nucleus divides, and each daughter nuclei is surrounded by a membrane. When the conditions are favourable again, the cyst dissolves and the daughter nuclei are released, which later develops into an individual cell. Plasmodium and Entamoeba undergo this process.
Budding
In this process, an outgrowth is produced from the cell from which a new organism is developed. The developed organism remains attached to the parent organism and detaches only when it matures, leaving behind scar tissue. The process is prominent in yeast and hydra.
Also refer: Budding
Vegetative propagation
In this, a new plant grows from the fragments of the parent plant or a specialized reproductive structure. The offspring are the exact clones of the original plant and there is no mixing of DNA. The common forms of vegetative propagations are grafting, layering, cutting, tuber, tissue culture, etc.
Regeneration
In organisms like Hydra and Planaria we had observed that if they are cut into several pieces, each part grows into a new organism. This is known as regeneration. The specialized cells proliferate and produce a large number of cells. These proliferated cells undergo changes and form different cells and tissues. The sequential process of these changes is known as development.
Spore Formation
During spore formation, the organisms form knob-like structures called a sporangium. This happens during unfavourable conditions in an inadequate supply of moisture and nutrients. When the conditions are favourable, they begin to grow.
The sporangia contain spores that develop into new individuals. The spores are covered by thick walls that protect the spores until they come in contact with moisture and begin to grow.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a natural way of reproduction and takes place in all multicellular organisms. This process involves two individuals to produce offspring. In this, the male and the female gametes fuse together and give rise to a new cell.
Sexual reproduction in Plants
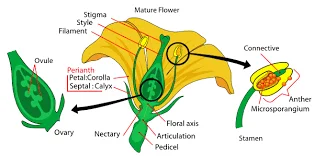
The angiosperms have both the male and female reproductive organs. The pollen grains produce male gametes which fuse with the egg cell of the female. The formation of gametes is known as gametogenesis. The pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of the flower. These pollens travel through the style and reach the female gametes present in the ovule. The two gametes fuse together and this process is known as fertilization. A zygote is formed which gets converted into an embryo. These give rise to a new seed which gradually turns into a fruit.
Sexual Reproduction in Humans
The testes in males and the ovaries in females are responsible for the production of sperm in males and eggs in females. The sperm fuses with the egg during fertilization, which results in the formation of a zygote and gets implanted in the wall of the uterus. It further divides and forms an embryo. The embryo starts developing week by week seeking nutrition from the mother with the help of the placenta. A new individual finally forms after a period of nine months.

CBSE Class 10 NCERT Science Topics for a Strong Foundation (NCERT DOWNLOAD)
| CHAPTER NAME | UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS |
| Topic Number | Topics |
| 7.1 | Reproduction in Plants and Animals |
| 7.2 | Reproductive Health |
| 7.3 | Safe Sex Vs HIV/AIDS |
| 7.4 | Child Bearing and Women Health |
Key Points on How do organisms reproduce
-
Reproduction is the process of producing new individuals of the same kind.
-
Organisms reproduce in two ways- asexually and sexually.
-
Asexual reproduction does not involve the fusion of male and female gametes. This takes place in bacteria, amoeba, hydra, etc.
-
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes and can be seen in humans and many animals.
-
Fission, budding, vegetative propagation, fragmentation are some different types of asexual reproduction. It does not require any reproductive organs.
-
Sexual reproduction involves the reproductive organs of male and female.
Learn more in detail about reproduction, its importance, process, types and other related topics at Testprepkart Biology.
Human Reproduction:
In humans, sexual reproduction involves complex processes within the male and female reproductive systems. Male reproductive organs produce sperm, while female reproductive organs produce eggs. Fertilization occurs in the female reproductive tract, leading to embryonic development and eventually the birth of offspring.
CBSE Class 10 Board Exam Sample Paper

[Previous Year Question Solution Maths Download Button]
[Previous Year Question Solution Science Download Button]
| CBSE CLASS 10 Mathematics Chapters |
| Chapter1: Real Numbers |
| Chapter2: Polynomials |
| Chapter3: Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables |
| Chapter4: Quadratic Equations |
| Chapter5: Arithmetic Progressions |
| Chapter6: Triangles |
| Chapter7: Coordinate Geometry |
| Chapter8: Introduction to Trigonometry |
| Chapter9: Some Applications of Trigonometry |
| Chapter10: Circles |
| Chapter11: Areas Related to Circles |
| Chapter12: Surface Areas and Volumes |
| Chapter13: Statistics |
| Chapter14: Probability |
| CBSE CLASS 10 Science Chapters |
| Chapter1: Chemical Reactions and Equations |
| Chapter2: Acids, Bases and Salts |
| Chapter3: Metals and Non-metals |
| Chapter4: Carbon and its Compounds |
| Chapter5: Life Processes |
| Chapter6: Control and Coordination |
| Chapter7: How do Organisms Reproduce? |
| Chapter8: Heredity |
| Chapter9: Light – Reflection and Refraction |
| Chapter10: The Human Eye and the Colourful World |
| Chapter11: Electricity |
| Chapter12: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current |
| Chapter13: Our Environment |
| Class 8 |
| Class 9 |
| Class 11 |
| Class 12 |
CBSE Class 10th Downloadable Resources:
| 1. CBSE Class 10th Topic Wise Summary | View Page / Download |
| 2. CBSE Class 10th NCERT Books | View Page / Download |
| 3. CBSE Class 10th NCERT Solutions | View Page / Download |
| 4. CBSE Class 10th Exemplar | View Page / Download |
| 5. CBSE Class 10th Previous Year Papers | View Page / Download |
| 6. CBSE Class 10th Sample Papers | View Page / Download |
| 7. CBSE Class 10th Question Bank | View Page / Download |
| 8. CBSE Class 10th Topic Wise Revision Notes | View Page / Download |
| 9. CBSE Class 10th Last Minutes Preparation Resources (LMP) | View Page / Download |
| 10. CBSE Class 10th Best Reference Books | View Page / Download |
| 11. CBSE Class 10th Formula Booklet | View Page / Download |
Being in CBSE class 10th and considering the board examinations you must be needing resources to excel in your examinations. At TestprepKart we take great pride in providing CBSE class 10th all study resources in downloadable form for you to keep you going.
Below is the list of all CBSE class 10th Downloads available on TestprepKart for both Indian and NRI students preparing for CBSE class 10th in UAE, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait & Bahrain.
FAQ
Q1: What is the purpose of reproduction in organisms?
A: Reproduction is vital for the continuity of species, ensuring the passing on of genetic information to subsequent generations and contributing to the adaptability and survival of organisms.
Q2: What are the main types of reproduction in organisms?
A: Organisms can reproduce through asexual and sexual means. Asexual reproduction involves a single parent, producing genetically identical offspring, while sexual reproduction involves the fusion of gametes from two parents, resulting in genetically diverse offspring.
Q3: How does asexual reproduction occur?
A: Asexual reproduction methods include binary fission (cell division), budding (outgrowth from a parent), fragmentation (breaking into fragments), and vegetative propagation (growth from plant structures).
Q4: What are the advantages of asexual reproduction?
A: Asexual reproduction allows for rapid multiplication of offspring, efficient colonization of favorable environments, and the conservation of energy since no mate is required.
Q5: What is sexual reproduction, and how does it work?
A: Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes. Male and female reproductive organs produce gametes, and fertilization results in genetically diverse offspring.
Leave a Reply