In the fascinating world of mathematics, where numbers dance and equations paint a vivid picture, the concept of zeroes of a polynomial holds a special place. As students delve into Class 10 mathematics, understanding the geometrical significance of these zeroes becomes crucial for unraveling the mysteries of algebra.
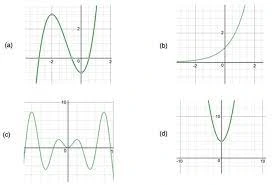
Let's embark on a journey to explore the geometrical meaning of the zeroes of a polynomial and discover the visual language that connects algebraic expressions to geometric shapes.
Exploring the Visual Poetry of Algebra: Unveiling the Geometric Dance of Polynomial Zeroes in Class 10 Mathematics
Degree of a Polynomial
The highest power of the variable of a given polynomial is called the degree of a polynomial. For example, the linear polynomial has a degree of 1, the quadratic polynomial has a degree of 2, the degree of the cubic polynomial is 3, and so on.
Zero of the Polynomial
The zero of a polynomial P(x), when x=k is the value obtained by substituting x as “k”, where k is a real number.It means that a real number k is the zero of a polynomial p(x) if p(k)=0.Now, let us discuss the geometrical meaning of the zeroes of a linear polynomial and quadratic polynomial in detail.
Geometrical Meaning of the Zeroes of a Polynomial Examples
Geometrical Meaning of Zeroes of Linear Polynomial:
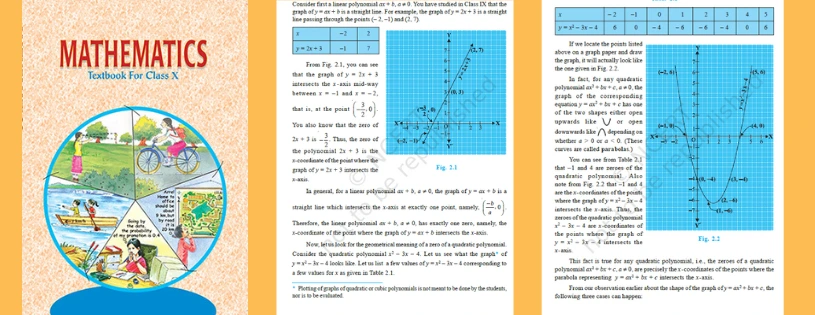
We know that a linear polynomial is in the form ax+b, where a ≠0. The graph of the linear equation, say y=ax+b is a straight line. Assume that the graph y=2x+3 is a polynomial. It means that y=2x+3 is a straight line that passes through the points (-2, -1) and (2, 7).In general, we can say that a linear polynomial ax+b, where a≠0, has exactly one zero. The zero of the linear polynomial is the x-coordinate of the point where the graph of y=ax+b intersects at the x-axis.
Geometrical Meaning of Zeroes of Quadratic Polynomial
We know that the standard form of a quadratic polynomial is ax2+bx+c, where a≠0. Now, let us understand the geometrical meaning of zeroes of quadratic polynomials with the help of an example.Consider the quadratic equation, y= x2-3x-4For the given quadratic equation, first find the coordinates (x, y), by taking a few values of x.
Connecting Algebra to Geometry
Now, let's bridge the gap between algebra and geometry. The zeroes of a polynomial are closely linked to the points where the graph of the polynomial intersects the x-axis. In other words, if x=c is a zero of the polynomial, then the graph of the polynomial will touch or cross the x-axis at the point
Role of Degree in Geometry
The degree of a polynomial also plays a significant role in understanding its geometric behavior. The degree determines the number of times a polynomial can intersect the x-axis. For instance, a quadratic polynomial (degree 2) can intersect the x-axis at most twice, while a cubic polynomial (degree 3) can intersect at most three times.
Multiplicity and Tangency
In some cases, a zero of a polynomial may have a multiplicity greater than 1. This multiplicity reflects the number of times the graph touches or crosses the x-axis at that particular zero. If a zero has multiplicity 2, the graph may touch the x-axis at that point without crossing it, indicating a tangent relationship
CBSE Class 10th Downloadable Resources:
| 1. CBSE Class 10th Topic Wise Summary | View Page / Download |
| 2. CBSE Class 10th NCERT Books | View Page / Download |
| 3. CBSE Class 10th NCERT Solutions | View Page / Download |
| 4. CBSE Class 10th Exemplar | View Page / Download |
| 5. CBSE Class 10th Previous Year Papers | View Page / Download |
| 6. CBSE Class 10th Sample Papers | View Page / Download |
| 7. CBSE Class 10th Question Bank | View Page / Download |
| 8. CBSE Class 10th Topic Wise Revision Notes | View Page / Download |
| 9. CBSE Class 10th Last Minutes Preparation Resources (LMP) | View Page / Download |
| 10. CBSE Class 10th Best Reference Books | View Page / Download |
| 11. CBSE Class 10th Formula Booklet | View Page / Download |
Being in CBSE class 10th and considering the board examinations you must be needing resources to excel in your examinations. At TestprepKart we take great pride in providing CBSE class 10th all study resources in downloadable form for you to keep you going.
Below is the list of all CBSE class 10th Downloads available on TestprepKart for both Indian and NRI students preparing for CBSE class 10th in UAE, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait & Bahrain.
SAMPLE PRACTICE QUESTION
Q1: What is the geometrical interpretation of the zeroes of a polynomial?
Ans: The zeroes represent the x-values where the polynomial intersects the x-axis on a graph, capturing points where the polynomial evaluates to zero.
Q2: How do multiple zeroes impact the graphical representation of a polynomial?
Ans: Multiple zeroes influence the graph's behavior. Double zeroes may create points of inflection, while triple zeroes can result in flattened curves at the x-axis.
Q3: Can a polynomial have complex zeroes, and how are they depicted geometrically?
Ans: Yes, a polynomial can have complex zeroes. Geometrically, complex zeroes manifest as points that don't intersect the real axis but contribute to the polynomial's overall behavior.
Q4: What role does the multiplicity of a zero play in shaping the graph?
Ans: The multiplicity of a zero determines how many times the polynomial touches or crosses the x-axis at that point, influencing the graph's slope and curvature.
Q5: Can a polynomial have repeated zeroes, and if so, how does it affect the graph?
Ans: Yes, a polynomial may have repeated zeroes. The multiplicity of each zero impacts the graph's local behavior, affecting the slope and curvature around those points.

| CBSE CLASS 10 Mathematics Chapter |
| Chapter:1 Real Numbers |
| Chapter:2 Polynomials |
| > Introduction |
| > Relationship between Zeroes and Coefficients of a Polynomial |
| > Summary |
| Chapter:4 Quadratic Equations |
| Chapter:5 Arithmetic Progressions |
| Chapter:6 Triangles |
| Chapter:7 Coordinate Geometry |
| Chapter:8 Introduction to Trigonometry |
| Chapter:9 Some Applications of Trigonometry |
| Chapter:10 Circles |
| Chapter:11 Areas Related to Circles |
| Chapter:12 Surface Areas and Volumes |
| Chapter:13 Statistics |
| Chapter:14 Probability |
| CBSE CLASS 10 Science Chapter |
| hapter:1 Chemical Reactions and Equations |
| Chapter:2 Acids, Bases and Salts |
| Chapter:3 Metals and Non-metals |
| Chapter:4 Carbon and its Compounds |
| Chapter:5 Life Processes |
| Chapter:6 Control and Coordination |
| Chapter:7 How do Organisms Reproduce? |
| Chapter:8 Heredity |
| Chapter:9 Light – Reflection and Refraction |
| Chapter:10 The Human Eye and the Colourful World |
| Chapter:11 Electricity |
| Chapter:12 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current |
| Chapter:13 Our Environment |
| Class 8 |
| Class 9 |
| Class 11 |
| Class 12 |
Leave a Reply