In the cosmic ballet of the universe, where planets orbit, and objects traverse intricate paths, Sir Isaac Newton's laws stand as immutable principles shaping our understanding of motion. Among these, Newton's Second Law of Motion emerges as a beacon, revealing the profound relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.
What is Newton’s Second Law of Motion?
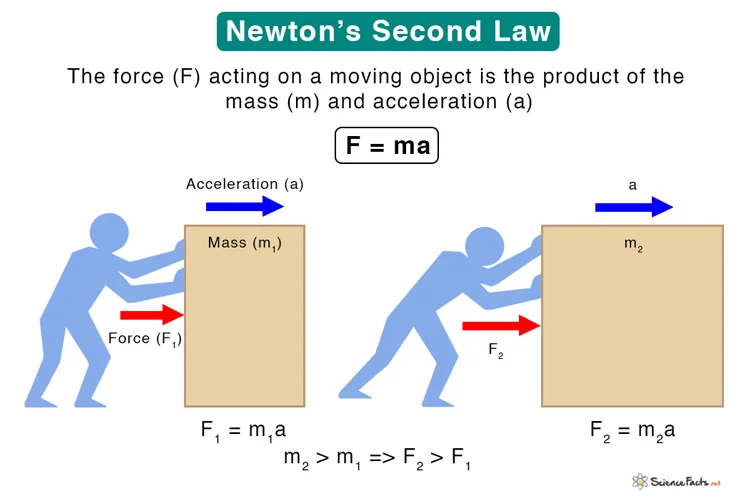
Newton's Second Law of Motion is a fundamental principle in classical mechanics that establishes a quantitative relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. It is expressed by the equation:
F=ma
Where:
F represents force,
m represents mass,
a represents acceleration.
The equation succinctly states that the force acting on an object is equal to the product of its mass and acceleration. This law provides a precise mathematical description of the cause-and-effect relationship between applied force, the resulting acceleration, and the object's mass.
Key Components of Newton's Second Law:
Force (F):
Force is any influence that can cause an object to undergo a change in speed, direction, or shape. It is measured in Newtons (N).
Mass (m):
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. It is a scalar quantity and is typically measured in kilograms (kg).
Acceleration (a):
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. It can involve an increase or decrease in speed, a change in direction, or both. Acceleration is measured in metres per second squared (m/s²).
Relationship between Force, Mass, and Acceleration:
Direct Proportionality:
Newton's Second Law states that force and acceleration are directly proportional. If you apply a greater force to an object, it will experience a greater acceleration, assuming the mass remains constant.
Inverse Proportionality:
The relationship between force and mass is inverse. If you increase the mass of an object, the acceleration it experiences for a given force will decrease, and vice versa.
Example Newton’s Second Law of Motion:
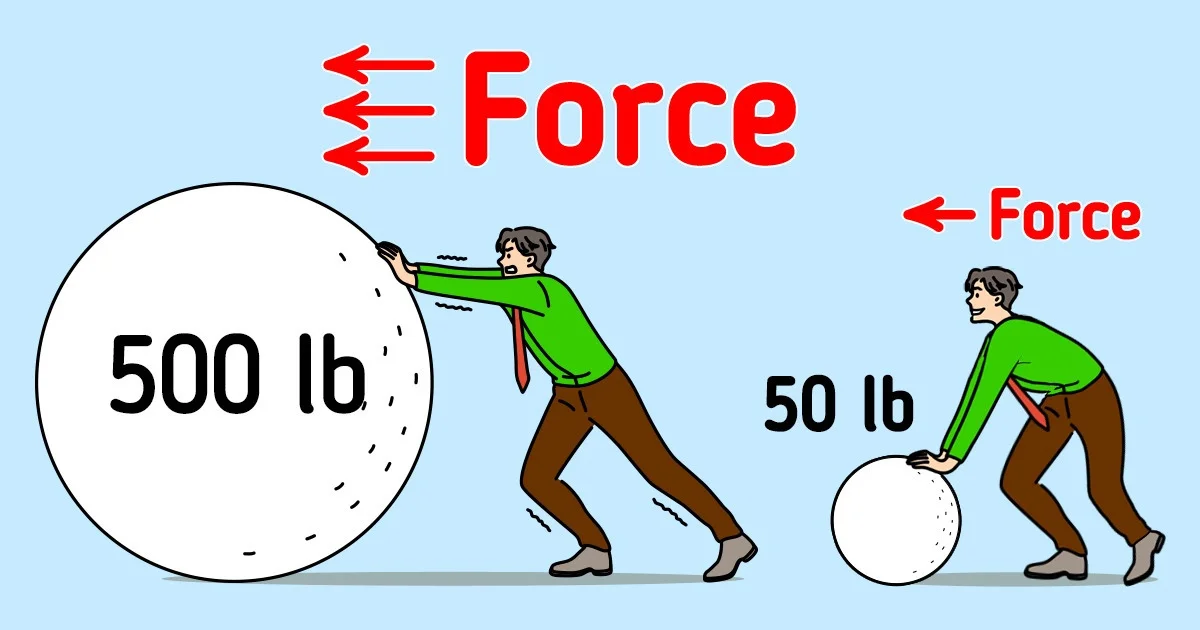
1· Try to move an object.
2· Pushing a car and a truck.
3· Racing Cars.
4· Rocket launch.
5· Kick the ball.
6· Car crash.
7· Two people walking.
8· Object thrown from a height

Newton’s Second Law Derivation:
Newton's Second Law of Motion, expressed as F=ma, provides a quantitative relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. To derive this law, let's consider the principles of dynamics and the fundamental concepts of force and motion.

Derivation Steps:
1. Definition of Force:
The force acting on an object is defined as the product of mass and acceleration:
F=m⋅a
2. Newton's Second Law:
Newton's Second Law states that the net force acting on an object is equal to the rate of change of its momentum with respect to time. For an object of constant mass, this can be expressed as:
F= dt /dp
Where p is the momentum of the object, given by p=m⋅v, where v is the velocity.
3. Substitution of Momentum:
Substitute the expression for momentum into the equation:
F= dt /d (m⋅v)
4. Application of Chain Rule:
Apply the chain rule to the derivative on the right side of the equation:
F=m⋅ dt/dv+v⋅ dt/dv
5. Assuming Constant Mass:
If we assume constant mass (dt/dm=0), the equation simplifies to:
F=m⋅dt/dv
This is the expression for force and acceleration, leading us to:
F=ma
This final form is the well-known Newton's Second Law of Motion, stating that the force acting on an object is equal to the product of its mass and acceleration.
CBSE Class 11th Downloadable Resources:
| 1. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Summary | View Page / Download |
| 2. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Books | View Page / Download |
| 3. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Solutions | View Page / Download |
| 4. CBSE Class 11th Exemplar | View Page / Download |
| 5. CBSE Class 11th Previous Year Papers | View Page / Download |
| 6. CBSE Class 11th Sample Papers | View Page / Download |
| 7. CBSE Class 11th Question Bank | View Page / Download |
| 8. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Revision Notes | View Page / Download |
| 9. CBSE Class 11th Last Minutes Preparation Resources | View Page / Download |
| 10. CBSE Class 11th Best Reference Books | View Page / Download |
| 11. CBSE Class 11th Formula Booklet | View Page / Download |
Being in CBSE class 11th and considering the board examinations you must be needing resources to excel in your examinations. At TestprepKart we take great pride in providing CBSE class 11th all study resources in downloadable form for you to keep you going.
Below is the list of all CBSE class 11th Downloads available on TestprepKart for both Indian and NRI students preparing for CBSE class 11th in UAE, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait & Bahrain.
SAMPLE PRACTICE QUESTIONS OF SIGNIFICANT FIGURES :
Q1. What is Newton's Second Law of Motion?
Answer: Newton's Second Law states that the force acting on an object is equal to the mass of that object multiplied by its acceleration. Mathematically, it is expressed as F=ma, where F is force,m is mass, and a is acceleration.
Q2. How Does Newton's Second Law Relate to the First Law?
Answer: Newton's First Law (Law of Inertia) states that an object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net external force. Newton's Second Law builds upon this by quantifying the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.
Q3. What Does Newton's Second Law Tell Us About Force?
Answer: Newton's Second Law provides a quantitative measure of force. It tells us that the force acting on an object is directly proportional to the acceleration it experiences, and the proportionality constant is the object's mass.
Q4. How Does Mass Affect Acceleration According to Newton's Second Law?
Answer: According to Newton's Second Law, acceleration is inversely proportional to mass. A smaller mass will experience a greater acceleration for a given force, while a larger mass will experience a smaller acceleration for the same force.
Q5. What Units are Used in Newton's Second Law?
Answer: In the International System of Units (SI), force is measured in Newtons (N), mass in kilograms (kg), and acceleration in meters per second squared (2m/s2).

| Class 11th CBSE Physics Chapters |
| Chapter1: UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS |
| Chapter2: MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE |
| Chapter3: MOTION IN A PLANE |
| Chapter4: LAWS OF MOTION |
| > Introduction |
| > Aristotle’s fallacy |
| > The law of inertia |
| > Newton’s first law of motion |
| > Newton’s third law of motion |
| > Conservation of momentum |
| > Equilibrium of a particle |
| > Common forces in mechanics |
| > Circular motion |
| > Solving problems in mechanics |
| Chapter5: WORK, ENERGY AND POWER |
| Chapter6: SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION |
| Chapter7: GRAVITATION |
| Chapter8: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS |
| Chapter9: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS |
| Chapter10: THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER |
| Chapter12: KINETIC THEORY |
| Chapter13: OSCILLATIONS |
| Chapter14: WAVES |
| Class 11th CBSE Chemistry Chapters |
| Chapter1: SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY |
| Chapter2: STRUCTURE OF ATOMS |
| Chapter3: CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES |
| Chapter4: CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE |
| Chapter5: THERMODYNAMICS |
| Chapter6 : EQUILIBRIUM |
| Chapter7: REDOX REACTIONS |
| Chapter8: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY – SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES |
| Chapter9: Hydrocarbons HYDROCARBONS |
| Class 11th CBSE Mathematics chapter |
| Chapter1: SETS |
| Chapter2: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter3: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter4: COMPLEX NUMBER AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS |
| Chapter5: LINEAR INEQUALITIES |
| Chapter6: PERMUTATIONS AND COMBINATIONS |
| Chapter7: BINOMIAL THEOREM |
| Chapter8: SEQUENCES AND SERIES |
| Chapter9: STRAIGHT LINES |
| Chapter10: CONIC SECTIONS |
| Chapter11: INTRODUCTION TO THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY |
| Chapter12: LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES |
| Chapter13: STATISTICS |
| Chapter14: PROBABILITY |
| Class 8 Link soon |
| Class 9 Link soon |
| Class 10 Link soon |
| Class 12 Link soon |
Leave a Reply