In the fast-paced world we navigate daily, the terms "stress" and "strain" have become integral aspects of our lives, impacting our physical and mental well-being. Stress, often a reaction to external pressures, can manifest in various forms, affecting individuals on both a personal and societal level. Meanwhile, strain refers to the internal consequences of this stress, influencing our emotions, relationships, and overall resilience. Exploring the intricacies of stress and strain unveils a complex interplay between external challenges and our internal responses. This blog will delve into understanding, managing, and mitigating the effects of stress and strain for a healthier and more balanced life.
Unveiling the Dynamics of Stress and Strain
What is Stress?
Stress is a natural response that our body and mind experience when facing challenges or demands. It is the body's way of mobilizing resources to cope with perceived threats or pressures. When confronted with a stressor, be it physical, emotional, or psychological, the body releases stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, triggering the "fight or flight" response.
Types of Stress
Stress manifests in different forms, each with its unique characteristics and impacts on our well-being. Here are some common types of stress:
- Tensile Stress: Tensile stress is a type of mechanical stress that occurs when a material is subjected to stretching or pulling forces. It is the force per unit area applied in the direction of the material's length, causing the material to elongate or deform. Tensile stress is denoted by the symbol σ (sigma) and is expressed in units of force per unit area, such as Pascals (Pa) or megapascals (MPa).
- Compressive Stress: Compressive stress is a type of mechanical stress that occurs when a material is subjected to compressive forces, meaning forces that act to squeeze or shorten the material. It is the force per unit area applied in the direction opposite to the material's natural tendency to elongate or expand. Compressive stress is denoted by the symbol σ (sigma) and is expressed in units of force per unit area, such as Pascals (Pa) or megapascals (MPa).
What is Strain?
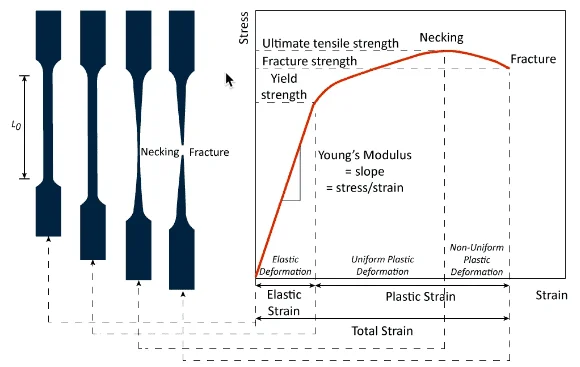
Strain, in the context of materials science and physics, refers to the deformation or change in shape that a material undergoes in response to applied forces. It is a measure of how much a material stretches or compresses relative to its original size or shape. Strain is often expressed as a dimensionless quantity or as a percentage.
Types of Strain:
Strain is a measure of the deformation or change in shape that a material undergoes in response to applied forces. There are various types of strain, each corresponding to different deformation scenarios. Here are the main types of strain:
- Tensile Strain: Tensile strain is a type of strain that occurs when a material is subjected to stretching or tensile forces, leading to an increase in its length. It is a measure of the relative deformation or elongation of the material under the influence of applied tensile stress.
- Compressive Strain: Compressive strain is a measure of the deformation or contraction experienced by a material when subjected to compressive or squeezing forces. It quantifies the relative change in length of the material under the influence of applied compressive stress.
As you delve into the intricacies of stress and strain in your class 11 physics curriculum, remember that these concepts extend far beyond equations and formulas. They form the backbone of structural analysis, materials science, and engineering. By comprehending the principles of stress and strain, you're laying a solid foundation for understanding how different materials respond to the forces that shape our physical world.

CBSE Class 11th Downloadable Resources:
| 1. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Summary | View Page / Download |
| 2. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Books | View Page / Download |
| 3. CBSE Class 11th NCERT Solutions | View Page / Download |
| 4. CBSE Class 11th Exemplar | View Page / Download |
| 5. CBSE Class 11th Previous Year Papers | View Page / Download |
| 6. CBSE Class 11th Sample Papers | View Page / Download |
| 7. CBSE Class 11th Question Bank | View Page / Download |
| 8. CBSE Class 11th Topic Wise Revision Notes | View Page / Download |
| 9. CBSE Class 11th Last Minutes Preparation Resources | View Page / Download |
| 10. CBSE Class 11th Best Reference Books | View Page / Download |
| 11. CBSE Class 11th Formula Booklet | View Page / Download |
Being in CBSE class 11th and considering the board examinations you must be needing resources to excel in your examinations. At TestprepKart we take great pride in providing CBSE class 11th all study resources in downloadable form for you to keep you going.
Below is the list of all CBSE class 11th Downloads available on TestprepKart for both Indian and NRI students preparing for CBSE class 11th in UAE, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait & Bahrain.
SAMPLE PRACTICE QUESTIONS OF SIGNIFICANT FIGURES :
Q1. What is stress, and how is it different from strain?
Answer: Stress is the internal force per unit area within a material, while strain is the relative change in shape or deformation experienced by the material. Stress is force-related, and strain is deformation-related.
Q2. Can you provide real-world examples of tensile and compressive stress?
Answer: Tensile stress can be observed when stretching a rubber band, while compressive stress is experienced by a column supporting a heavy load, causing it to shorten.
Q3. How are stress and strain related in materials science?
Answer: Stress and strain are related through material properties like Young's Modulus (E), which defines the stiffness of a material. The relationship is expressed as σ=E⋅ε.
Q4. What are the consequences of excessive stress or strain on materials?
Answer: Excessive stress or strain can lead to material failure, deformation, or structural damage. Understanding these limits is crucial in engineering and design.
Q5. How does shear stress differ from tensile and compressive stress?
Answer: Shear stress occurs when forces act parallel to the surface of a material, causing it to deform by sliding or twisting. Tensile and compressive stress, on the other hand, act perpendicular to the surface.

| Class 11th CBSE Physics Chapters |
| Chapter1: UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS |
| Chapter2: MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE |
| Chapter3: MOTION IN A PLANE |
| Chapter4: LAWS OF MOTION |
| Chapter5: WORK, ENERGY AND POWER |
| Chapter6: SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION |
| Chapter7: GRAVITATION |
| Chapter8: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS |
| Chapter9: MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS |
| Chapter10: THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER |
| Chapter12: KINETIC THEORY |
| Chapter13: OSCILLATIONS |
| Chapter14: WAVES |
| Class 11th CBSE Chemistry Chapters |
| Chapter1: SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY |
| Chapter2: STRUCTURE OF ATOMS |
| Chapter3: CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES |
| Chapter4: CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE |
| Chapter5: THERMODYNAMICS |
| Chapter6: EQUILIBRIUM |
| Chapter7: REDOX REACTIONS |
| Chapter8: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY – SOME BASIC PRINCIPLE AND TECHNIQUES |
| Chapter9: Hydrocarbons HYDROCARBONS |
| Class 11th CBSE Mathematics chapter |
| Chapter1: SETS |
| Chapter2: RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter3: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS |
| Chapter4: COMPLEX NUMBER AND QUADRATIC EQUATIONS |
| Chapter5: LINEAR INEQUALITIES |
| Chapter6: PERMUTATIONS AND COMBINATIONS |
| Chapter7: BINOMIAL THEOREM |
| Chapter8: SEQUENCES AND SERIES |
| Chapter9: STRAIGHT LINES |
| Chapter10: CONIC SECTIONS |
| Chapter11: INTRODUCTION TO THREE-DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY |
| Chapter12: LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES |
| Chapter13: STATISTICS |
| Chapter14: PROBABILITY |
| Class 8 Link soon |
| Class 9 Link soon |
| Class 10 Link soon |
| Class 12 Link soon |
Leave a Reply